In-Mold Labeling (IML) Mold: A Comprehensive Guide

What is an In-Mold Labeling Mold?
An In-Mold Labeling (IML) mold is a specialized component in plastic manufacturing that works in conjunction with labeling robots to embed pre-printed labels directly into plastic products during the injection molding process. This technology creates a permanent bond between the label and the plastic surface, resulting in a seamless, high-quality finish that enhances product appearance and durability.
Working Principle
The IML robot operates through a precise sequence:
1.A pre-printed label (on PP, PE, or other materials) is loaded into the system
2.The robotic arm positions the label into the open mold cavity
3.Plastic resin is injected, encapsulating the label
4.The finished product emerges with the label permanently fused to its surface
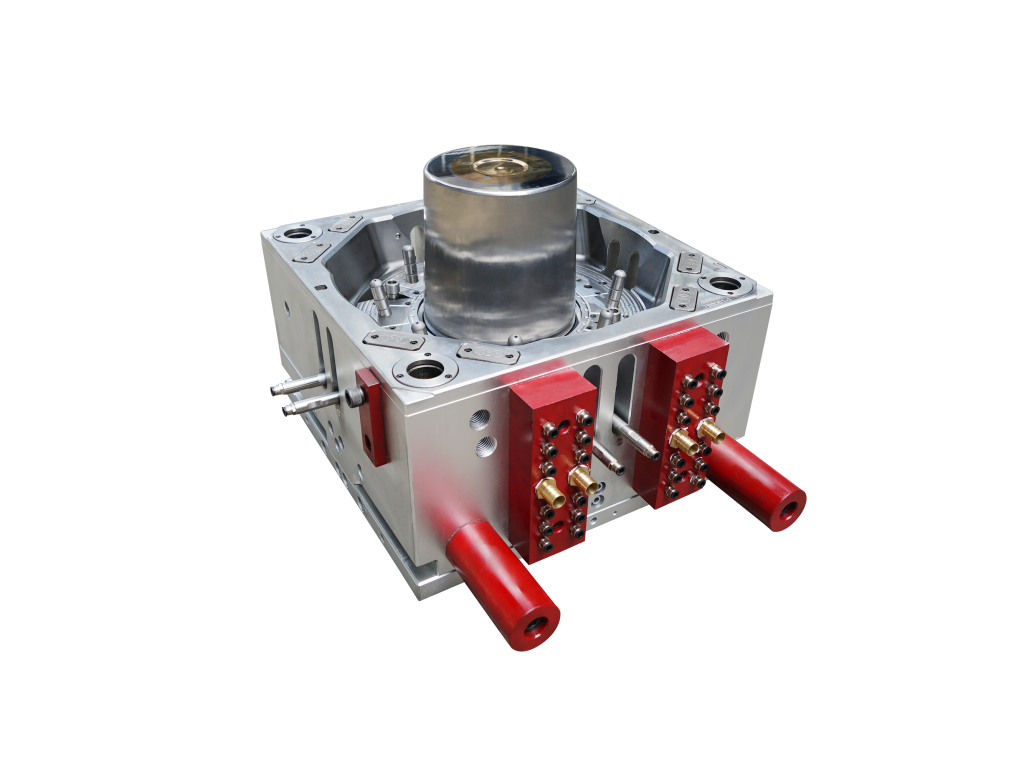
Key Components and Technical Specifications
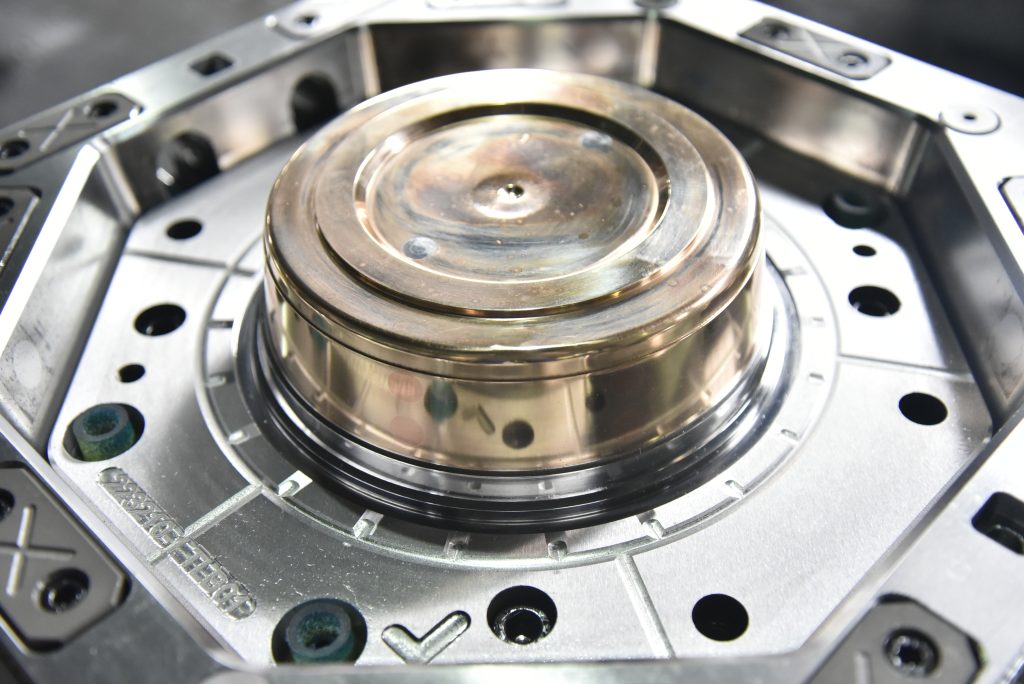
Mold Structure
Cavity Design: Precision-engineered (±0.2mm tolerance) to accommodate label placement
Vacuum System: Ensures proper label adhesion before injection
Thermal Control: Maintains consistent temperature for optimal resin flow
Ejection System: Carefully designed to prevent label displacement
Material Composition
Mold Steel: Typically uses DC53 or H13 alloy steel for durability and heat resistance
Label Materials: PP/PE/PET films with thickness of 0.04-0.08mm
Adhesive Layer: Specialized thermal bonding agents activated by molten plastic
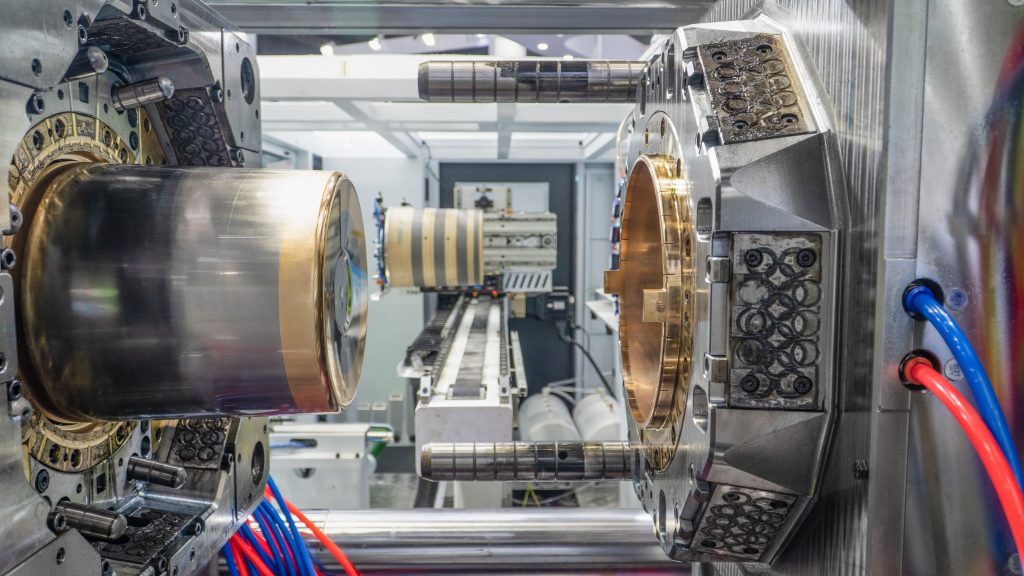
Integration with Robotic Systems
Synchronization Process
1.The robot receives mold opening signal
2.Picks up label from feeding station
3.Positions label into mold cavity using electrostatic or vacuum methods
4.Confirms placement before mold closes
5.Coordinates with injection timing for perfect resin encapsulation
Technical Requirements
Cycle time synchronization (3-25 seconds)
Repeatable positioning accuracy (±0.05mm)
Temperature resistance (up to 180°C)
Dust-free operation environment
Applications and Advantages Industry Applications
Food Packaging: Yogurt cups, butter boxes, ice cream containers
Cosmetics: Bottles, jars, and tubes
Medical: Sterile packaging for medical devices
Industrial: Chemical containers and automotive parts
Key Benefits
1.Enhanced Aesthetics: “No-label” look with high-quality graphics
2.Durability: Labels resist scratching, peeling, and fading
3.Efficiency: Eliminates secondary labeling operations
4.Cost Savings: Reduces labor and material waste
5.Sustainability: Easier recycling of mono-material containers
